XGBoost Model Analysis
The third approach in our analytical exploration was the implementation of the XGBoost model, which employs ensemble learning using multiple algorithms, like decision trees, to enhance performance.
Gradient boosting techniques were used to minimize loss by adjusting the model iteratively based on errors, complemented by SMOTE and optimized hyperparameters for efficient training and performance.
Data Cleaning
Consistent with our prior models, we applied the same data cleaning procedures, encoding categorical variables like 'Gender' and 'Geography' into binary columns, and further refined the dataset by excluding less impactful features identified during training.
Model Training and Results
The Standard Scaler method was included to normalize the test and training data. The hyperparameters configured for the XGBoost model were:
- Learning Rate: 0.1
- n_estimators: 100
- Max Depth: 5
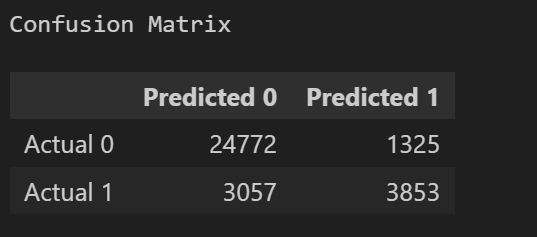
The model achieved an accuracy score of approximately 86.73%.
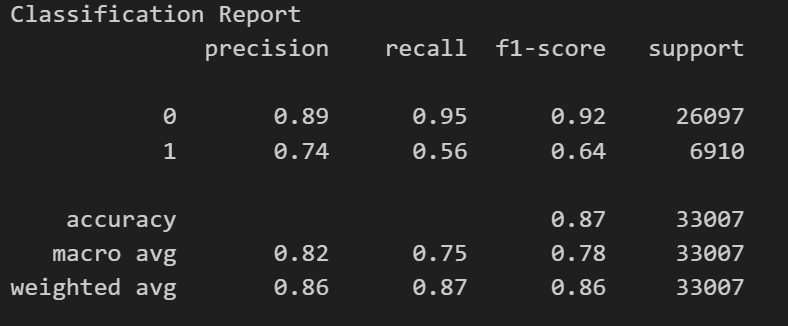
The following visualizations display the Confusion Matrix and Classification Report:
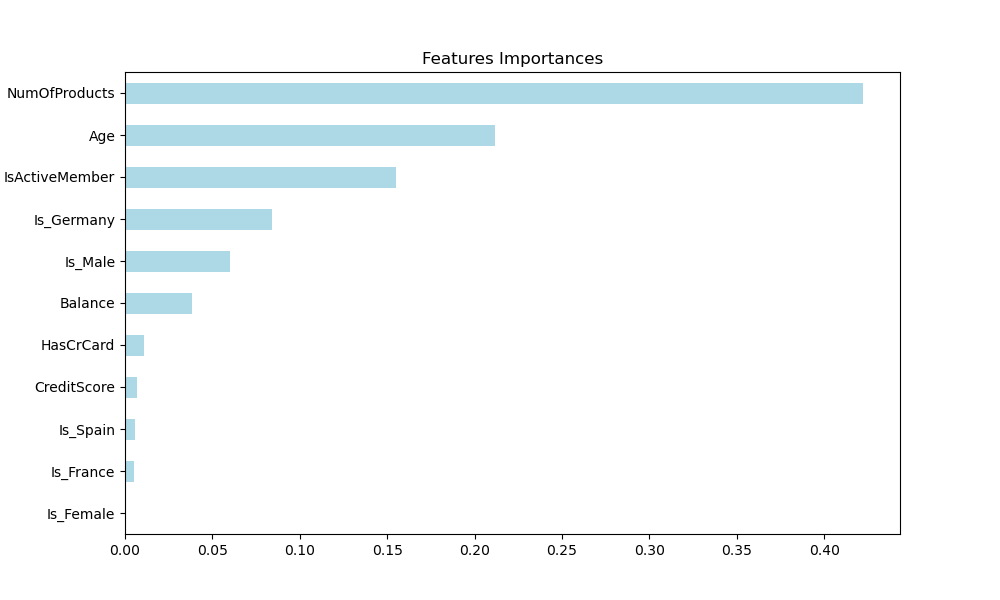
Findings
The XGBoost model demonstrated the highest accuracy among the tested models, with the SMOTE technique notably improving the prediction for class '1' (clients that are likely to leave), while maintaining robust predictions for class '0' (clients that stay).
We advocate for the XGBoost model due to its:
- Superior Accuracy
- Capability in Ensemble Learning
- Handling of Non-Linear Relationships
- Effectiveness against Overfitting with SMOTE
The Classification Report reflects a strong precision and recall for class '0' and a marked improvement for class '1'. To further enhance the model's accuracy, the acquisition of a larger dataset and the exploration of innovative techniques are recommended.